Secrets backend configuration
Description
Instead of manually filling in the Airflow connections and variables for every environment, you can also use the Airflow UI in Conveyor to load these automatically from an external backend (e.g. AWS Secrets Manager or Azure Key Vault). This makes it possible to specify them ones and automatically get the configuration in your environment. We integrate with the secret backend functionality for Airflow, as described here. In this how-to we will go over the different steps required to set this up using Conveyor.
Creating a secret
To start with, you will need to create the connection and/or variable secret in AWS or Azure.
- AWS
- Azure
For AWS we support configuring the secret in AWS secrets manager. In the UI you can configure it as follows: From the secrets manager page click on store a new secret. There select other type of secret and specify the secret content in json format.
More information on the structure of the json content can be found on the Airflow documentation As an example look at the following screenshot:

Click next next and specify a name for the secret, which we will use in a later step. Finally click on store to persist the secret in AWS secrets manager.
For Azure we support configuring the secret in Azure keyvault. In the UI you can configure it as follows: Search for key vaults and select it to go to the keyvaults home page. Now you can either create a new keyvault, by clicking the create button, or select an already existing keyvault.
In your Keyvault, you can create a new secret by clicking the secrets icon in the left tab. Click on generate/import and specify the name, which we will need in a later step, as well as the secret content in json format.
More information on the structure of the json content can be found on the Airflow documentation As an example look at the following screenshot:
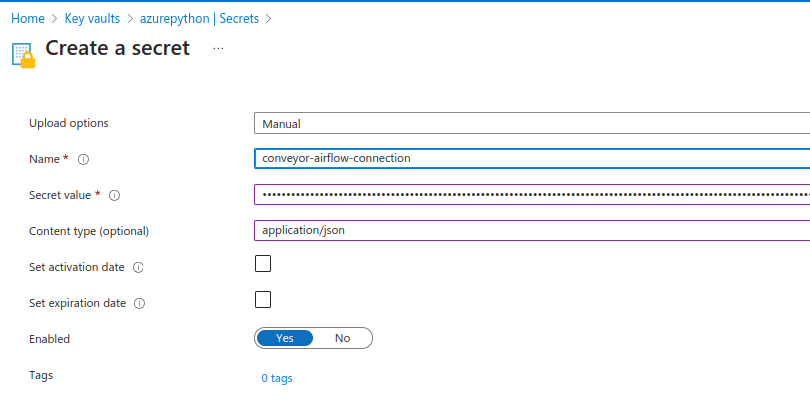
Click on create to store the secret in the Azure keyvault.
Creating an IAM identity
In order for Airflow to be able to read the secret values, you will need to attach an IAM identity.
- AWS
- Azure
For AWS you will need to create an AWS role which has permissions to read as well as describe the secrets in secretsmanager.
The following actions are required for the integration to work: secretsmanager:GetSecretValue and secretsmanager:DescribeSecret.
One way of creating the respective role is to use terraform, which will look similar to:
# create a IAM role that can be assumed by a given Airflow environment
resource "aws_iam_role" "airflow_secrets_backend_role" {
name = "airflow-secrets-backend-role"
assume_role_policy = data.aws_iam_policy_document.airflow_secret_assume_policy.json
}
data "aws_iam_policy_document" "airflow_secret_assume_policy" {
statement {
actions = ["sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity"]
effect = "Allow"
condition {
test = "StringLike"
variable = "${var.oidc_url}:sub"
values = ["system:serviceaccount:<conveyor-environment>:airflow-<conveyor-environment>"]
}
principals {
identifiers = ["arn:aws:iam::${var.aws_account_id}:oidc-provider/${var.oidc_url}"]
type = "Federated"
}
}
}
# Allow the IAM role to access certain secrets in AWS secrets manager
resource "aws_iam_role_policy" "airflow_secret_access" {
name = "airflow-secret-access"
role = aws_iam_role.airflow_secrets_backend_role.id
policy = data.aws_iam_policy_document.airflow_secret_access.json
}
data "aws_iam_policy_document" "airflow_secret_access" {
statement {
actions = [
"secretsmanager:GetSecretValue",
"secretsmanager:DescribeSecret",
]
resources = [
"arn:*:secretsmanager:*:*:secret:<your-secret-name>-??????",
]
effect = "Allow"
}
}
The your-secret-name in resources section should be changed to reflect the secret name that you have created in the first step of this how-to guide.
The oidc_url of the eks cluster can be using the conveyor_cluster datasource, when using terraform, or by using the conveyor CLI and running: conveyor cluster list
The arn of a secret in secretmanager is the name of your secret with a random 6 character suffix, which is why the -?????? is added at the end.
For Azure you will need to create an Azure identity and give that identity access to read secrets in your Azure Keyvault.
You should add the following roles to the identity in your Keyvault: Key Vault Reader and Key Vault Secrets User.
One way to specify this configuration is to use terraform. An example configuration looks as follows:
#Create the Azure service principle
resource "azuread_application" "azure_airflow" {
display_name = "azure-airflow"
}
resource "azuread_service_principal" "azure_airflow" {
application_id = azuread_application.azure_airflow.application_id
app_role_assignment_required = false
}
# Allow the Kubernetes cluster to fetch tokens for the service principal
resource "azuread_application_federated_identity_credential" "azure_airflow" {
application_object_id = azuread_application.azure_airflow.object_id
display_name = "kubernetes-federated-identity-azureairflow"
audiences = ["api://AzureADTokenExchange"]
issuer = var.oidc_url
subject = "system:serviceaccount:<conveyor-environment>:airflow-<conveyor-environment>"
}
# Allow the service principal to read secrets in the respective keyvault.
resource "azurerm_role_assignment" "keyvault_read_airflow" {
scope = var.keyvault_id
role_definition_name = "Key Vault Reader"
principal_id = azuread_service_principal.azure_airflow.id
}
resource "azurerm_role_assignment" "keyvault_read_secret_airflow" {
scope = var.keyvault_id
role_definition_name = "Key Vault Secrets User"
principal_id = azuread_service_principal.azure_airflow.id
}
The variable keyvault_id can be retrieved from the keyvault where we created the secret, as described in the first step of this how-to guide.
The oidc_url of the aks cluster can be using the conveyor_cluster datasource, when using terraform, or by using the conveyor CLI and running: conveyor cluster list
Configuring the environment
The secret backend can be configured on an environment in three ways, namely:
CLI
The configuration settings can also be updated through the cli, through the use of the conveyor env update command.
Apart from the variable and connection configuration options, you must also specify the iam identity for the environment. In AWS this is the IAM role name and in Azure this is the application client id. The application client id can be found on the page of the app registration in the Azure portal.
For more details take a look at the CLI docs
Terraform
The configuration settings can also be specified in the environment resource in Terraform.
Apart from the variable and connection configuration options, you must also specify the iam identity for the environment. In AWS this is the role name and in Azure this is the application client id, which can be found on the page of the app registration in the Azure portal.
For more details take a look at the terraform docs
Conveyor UI
In the Conveyor UI, you can configure a secrets backend using the settings tab of the respective environment.
In the form section secrets-backend you can specify the necessary configuration. This form looks as follows:
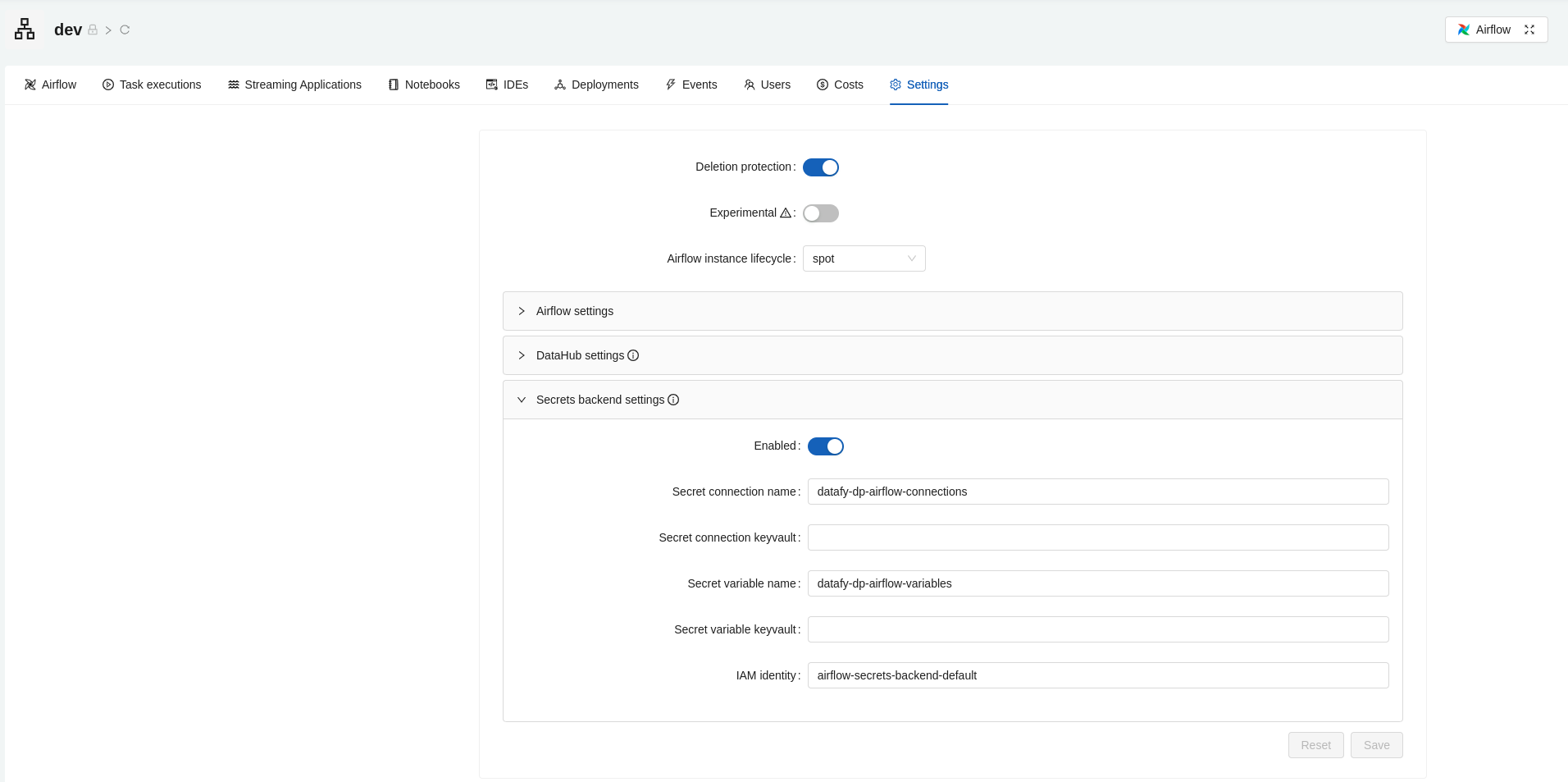
Frequently asked questions
If I update a secret in AWS secrets manager or Azure keyvault, will it automatically be updated in the environment?Yes, it will be updated after 5 minutes. We poll for changes every 5 minutes and update the environment accordingly.
I do not see my new variables/connections after updating an existing secret in AWS secrets manager or Azure keyvault in the Airflow UI, what is going on?Syncing the secrets with the Airflow UI is only done when the Airflow web container is started, this is not done periodically. Note: the values are updated though and you can use them in your tasks (see previous question), you just don't' see them in the Airflow UI yet.